
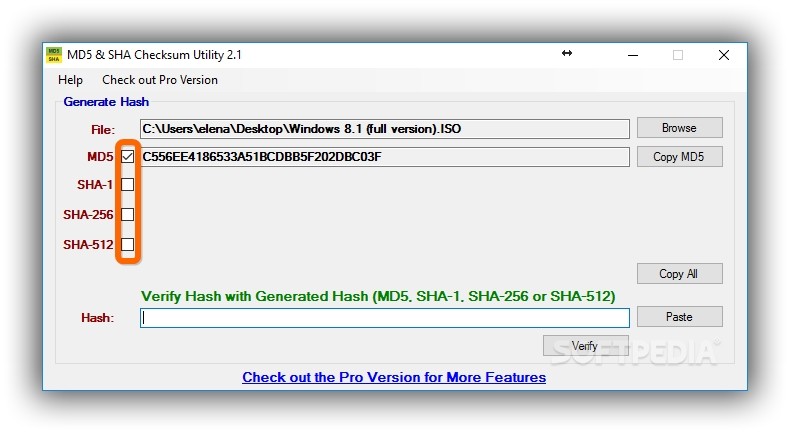
ExamplesĬalculate a checksum for the file ' /Users/jayden/Downloads/demo.dmg': The md5 utility exits 0 on success, and 1 if at least one of the input files could not be read. Drag the file into the Terminal window to complete the filename, then hit Return. The hexadecimal checksum of each file listed on the command line is printed after the options are processed. The options may be used in any combination and must precede any files named on the command line. SHA256 and SHA512 are better options as they have been more resilient to attacks (as of 2009). So MD5 should be avoided when creating new protocols, or implementing protocols with better options. MD5's designer Ron Rivest has stated "md5 and sha1 are both clearly broken (in terms of collision-resistance)".

The MD5 algorithm is intended for digital signature applications, where a large file must be 'compressed' in a secure manner before being encrypted with a private (secret) key under a public-key cryptosystem such as RSA.

It is conjectured that it is computationally infeasible to produce two messages having the same message digest, or to produce any message having a given prespecified target message digest. The md5 utility takes as input a message of arbitrary length and produces as output a 'fingerprint' or 'message digest' of the input. This helps with visual diffs.ĭoes nothing when combined with the -ptx options. q Quiet mode - only the checksum is printed out. p Echo stdin to stdout and append the checksum to stdout. Calculate a message-digest fingerprint (checksum) for a file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
